








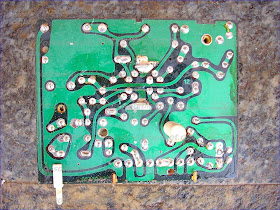
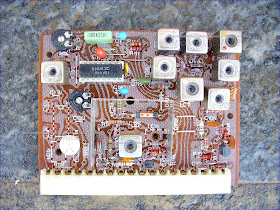



RADIOMARELLI TV12P B/W CHASSIS RV 674 SH 12 P 842.203.011
It's a modular chassis so friendly to service.
Sound unit:687.345.810/A with TDA1190 (Fairchild)
Synch unit:687.305.010/A with ITT TBA950-1
If ampl + Det + demod:687.345.710/B with TDA440
Frame unit: tda1270 -e
Line deflection output + EHT with BU407B AND Line transformer SAREA (Was long time ago a fabricant of transformers)
The tuning circuits has a large knob potentiometers tuning system which use voltage controlled capacitances such as varactor diodes as the frequency determining elements.
 Therefore a stable AFC circuit is developed:
Therefore a stable AFC circuit is developed: A
superheterodyne receiver having an automatic intermediate
frequency control circuit with means to prevent the faulty
regulation thereof. The receiver has means for receiving a radio
frequency signal and mixing the same with the output of a
superheterodyne oscillator. This produces an intermediate frequency
signal which is coupled to a frequency or phase discriminator to
produce an error signal for controlling the frequency of the
superheterodyne oscillator. A regulation circuit is provided having
an electronic switch to interrupt the feedback circuit when only
unwanted frequencies tend to produce faulty regulation of the
superheterodyne oscillator.
A
superheterodyne receiver having an automatic intermediate
frequency control circuit with means to prevent the faulty
regulation thereof. The receiver has means for receiving a radio
frequency signal and mixing the same with the output of a
superheterodyne oscillator. This produces an intermediate frequency
signal which is coupled to a frequency or phase discriminator to
produce an error signal for controlling the frequency of the
superheterodyne oscillator. A regulation circuit is provided having
an electronic switch to interrupt the feedback circuit when only
unwanted frequencies tend to produce faulty regulation of the
superheterodyne oscillator. Power
Supply: The examples chosen are taken from manufacturers' circuit
diagrams and are usually simplified to emphasise the fundamental nature
of the circuit. For each example the particular transistor properties
that are exploited to achieve the desired performance are made clear. As
a rough and ready classification the circuits are arranged in order of
frequency: this part is devoted to circuits used at zero frequency,
field frequency and audio frequencies. Series Regulator Circuit Portable
television receivers are designed to operate from batteries (usually
12V car batteries) and from the a.c. mains. The receiver usually has an
11V supply line, and circuitry is required to ensure that the supply
line is at this voltage whether the power source is a battery or the
mains. The supply line also needs to have good regulation, i.e. a low
output resistance, to ensure that the voltage remains constant in spite
of variations in the mean current taken by some of the stages in the
receiver. Fig. 1 shows a typical circuit of the power -supply
arrangements. The mains transformer and bridge rectifier are designed to
deliver about 16V. The battery can be assumed to give just over 12V.
Both feed the regulator circuit Trl, Tr2, Tr3, which gives an 11V output
and can be regarded as a three -stage direct -coupled amplifier. The
first stage Tr 1 is required to give an output current proportional to
the difference between two voltages, one being a constant voltage
derived from the voltage reference diode D I (which is biased via R3
from the stabilised supply). The second voltage is obtained from a
preset potential divider connected across the output of the unit, and is
therefore a sample of the output voltage. In effect therefore Tr 1
compares the output voltage of the unit with a fixed voltage and gives
an output current proportional to the difference between them. Clearly a
field-effect transistor could do this, but the low input resistance of a
bipolar transistor is no disadvantage and it can give a current output
many times that of a field-effect transistor and is generally preferred
therefore. The output current of the first stage is amplified by the two
subsequent stages and then becomes the output current of the unit.
Clearly therefore Tr2 and Tr3 should be current amplifiers and they
normally take the form of emitter followers or common emitter stages
(which have the same current gain). By adjusting the preset control we
can alter the fraction of the output voltage' applied to the first stage
and can thus set the output voltage of the unit at any desired value
within a certain range. By making assumptions about the current gain of
the transistors we can calculate the degree of regulation obtainable.
For example, suppose the gain of Tr2 and Tr3 in cascade is 1,000, and
that the current output demanded from the unit changes by 0.1A (for
example due to the disconnection of part of the load). The corresponding
change in Tr l's collector current is 0.1mA and, if the standing
collector current of Tr 1 is 1mA, then its mutual conductance is
approximately 4OmA/V and the base voltage must change by 2.5mV to bring
about the required change in collector current. If the preset potential
divider feeds one half of the output voltage to Tr l's base, then the
change in output voltage must be 5mV. Thus an 0.1A change in output
current brings about only 5mV change in output voltage: this represents
an output resistance of only 0.0552.
Power
Supply: The examples chosen are taken from manufacturers' circuit
diagrams and are usually simplified to emphasise the fundamental nature
of the circuit. For each example the particular transistor properties
that are exploited to achieve the desired performance are made clear. As
a rough and ready classification the circuits are arranged in order of
frequency: this part is devoted to circuits used at zero frequency,
field frequency and audio frequencies. Series Regulator Circuit Portable
television receivers are designed to operate from batteries (usually
12V car batteries) and from the a.c. mains. The receiver usually has an
11V supply line, and circuitry is required to ensure that the supply
line is at this voltage whether the power source is a battery or the
mains. The supply line also needs to have good regulation, i.e. a low
output resistance, to ensure that the voltage remains constant in spite
of variations in the mean current taken by some of the stages in the
receiver. Fig. 1 shows a typical circuit of the power -supply
arrangements. The mains transformer and bridge rectifier are designed to
deliver about 16V. The battery can be assumed to give just over 12V.
Both feed the regulator circuit Trl, Tr2, Tr3, which gives an 11V output
and can be regarded as a three -stage direct -coupled amplifier. The
first stage Tr 1 is required to give an output current proportional to
the difference between two voltages, one being a constant voltage
derived from the voltage reference diode D I (which is biased via R3
from the stabilised supply). The second voltage is obtained from a
preset potential divider connected across the output of the unit, and is
therefore a sample of the output voltage. In effect therefore Tr 1
compares the output voltage of the unit with a fixed voltage and gives
an output current proportional to the difference between them. Clearly a
field-effect transistor could do this, but the low input resistance of a
bipolar transistor is no disadvantage and it can give a current output
many times that of a field-effect transistor and is generally preferred
therefore. The output current of the first stage is amplified by the two
subsequent stages and then becomes the output current of the unit.
Clearly therefore Tr2 and Tr3 should be current amplifiers and they
normally take the form of emitter followers or common emitter stages
(which have the same current gain). By adjusting the preset control we
can alter the fraction of the output voltage' applied to the first stage
and can thus set the output voltage of the unit at any desired value
within a certain range. By making assumptions about the current gain of
the transistors we can calculate the degree of regulation obtainable.
For example, suppose the gain of Tr2 and Tr3 in cascade is 1,000, and
that the current output demanded from the unit changes by 0.1A (for
example due to the disconnection of part of the load). The corresponding
change in Tr l's collector current is 0.1mA and, if the standing
collector current of Tr 1 is 1mA, then its mutual conductance is
approximately 4OmA/V and the base voltage must change by 2.5mV to bring
about the required change in collector current. If the preset potential
divider feeds one half of the output voltage to Tr l's base, then the
change in output voltage must be 5mV. Thus an 0.1A change in output
current brings about only 5mV change in output voltage: this represents
an output resistance of only 0.0552. Power supply
is realized with mains transformer and Linear transistorized power
supply stabilizer, A DC power supply apparatus includes a rectifier
circuit which rectifies an input commercial AC voltage. The
rectifier output voltage is smoothed in a smoothing capacitor.
Voltage stabilization is provided in the stabilizing circuits by the
use of Zener diode circuits to provide biasing to control the
collector-emitter paths of respective transistors.A linear regulator
circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention has an
input node receiving an unregulated voltage and an output node
providing a regulated voltage. The linear regulator circuit includes a
voltage regulator, a bias circuit, and a current control device.
Power supply
is realized with mains transformer and Linear transistorized power
supply stabilizer, A DC power supply apparatus includes a rectifier
circuit which rectifies an input commercial AC voltage. The
rectifier output voltage is smoothed in a smoothing capacitor.
Voltage stabilization is provided in the stabilizing circuits by the
use of Zener diode circuits to provide biasing to control the
collector-emitter paths of respective transistors.A linear regulator
circuit according to an embodiment of the present invention has an
input node receiving an unregulated voltage and an output node
providing a regulated voltage. The linear regulator circuit includes a
voltage regulator, a bias circuit, and a current control device.In one embodiment, the current control device is implemented as an NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) having a collector electrode forming the input node of the linear regulator circuit, an emitter electrode coupled to the input of the voltage regulator, and a base electrode coupled to the second terminal of the bias circuit. A first capacitor may be coupled between the input and reference terminals of the voltage regulator and a second capacitor may be coupled between the output and reference terminals of the voltage regulator. The voltage regulator may be implemented as known to those skilled in the art, such as an LDO or non-LDO 3-terminal regulator or the like.
The bias circuit may include a bias device and a current source. The bias device has a first terminal coupled to the output terminal of the voltage regulator and a second terminal coupled to the control electrode of the current control device. The current source has an input coupled to the first current electrode of the current control device and an output coupled to the second terminal of the bias device. A capacitor may be coupled between the first and second terminals of the bias device.
In the bias device and current source embodiment, the bias device may be implemented as a Zener diode, one or more diodes coupled in series, at least one light emitting diode, or any other bias device which develops sufficient voltage while receiving current from the current source. The current source may be implemented with a PNP BJT having its collector electrode coupled to the second terminal of the bias device, at least one first resistor having a first end coupled to the emitter electrode of the PNP BJT and a second end, a Zener diode and a second resistor. The Zener diode has an anode coupled to the base electrode of the PNP BJT and a cathode coupled to the second end of the first resistor. The second resistor has a first end coupled to the anode of the Zener diode and a second end coupled to the reference terminal of the voltage regulator. A second Zener diode may be included having an anode coupled to the cathode of the first Zener diode and a cathode coupled to the first current electrode of the current control device.
 A circuit is disclosed for improving
operation of a linear regulator, having an input terminal, an
output terminal, and a reference terminal. The circuit includes an
input node, a transistor, a bias circuit, and first and second
capacitors. The transistor has a first current electrode coupled to
the input node, a second current electrode for coupling to the
input terminal of the linear regulator, and a control electrode. The
bias circuit has a first terminal for coupling to the output
terminal of the linear regulator and a second terminal coupled to
the control electrode of the transistor. The first capacitor is for
coupling between the input and reference terminals of the linear
regulator, and the second capacitor is for coupling between the
output and reference terminals of the linear regulator. The bias
circuit develops a voltage sufficient to drive the control terminal
of the transistor and to operate the linear regulator. The bias
circuit may be a battery, a bias device and a current source, a
floating power supply, a charge pump, or any combination thereof.
The transistor may be implemented as a BJT or FET or any other
suitable current controlled device.
A circuit is disclosed for improving
operation of a linear regulator, having an input terminal, an
output terminal, and a reference terminal. The circuit includes an
input node, a transistor, a bias circuit, and first and second
capacitors. The transistor has a first current electrode coupled to
the input node, a second current electrode for coupling to the
input terminal of the linear regulator, and a control electrode. The
bias circuit has a first terminal for coupling to the output
terminal of the linear regulator and a second terminal coupled to
the control electrode of the transistor. The first capacitor is for
coupling between the input and reference terminals of the linear
regulator, and the second capacitor is for coupling between the
output and reference terminals of the linear regulator. The bias
circuit develops a voltage sufficient to drive the control terminal
of the transistor and to operate the linear regulator. The bias
circuit may be a battery, a bias device and a current source, a
floating power supply, a charge pump, or any combination thereof.
The transistor may be implemented as a BJT or FET or any other
suitable current controlled device.INTEGRATED circuits are slowly but surely taking over more and more of the circuitry used in television sets even B/W.
The first step, some many years ago now, was to wrap the 6MHz intercarrier sound strip into a neat package such as the TAA350 or TAA570. Then came the "jungle" i.c. which took over the sync separator and a.g.c. operations. Colour receiver decoder circuitry was the next obvious area to be parcelled up in i.c. form, two i.c. decoder and the more sophisticated Philips four i.c. design was coming on the scene. The latter is about to be superseded by a three i.c. version in which the TBA530 and TBA990 are replaced by the new TCA800 which provides chrominance signal demodulation, matrixing, clamping and preamplification, with RGB outputs of typically 5V peak -to -peak.
To improve performance a number of sets adopted a synchronous detector i.c.-the MC1330P -for vision demodulation, which of course overcomes the problem of quadrature distortion. In one monochrome chassis this i.c. is partnered by a complete vision i.f. strip i.c., the MC1352P. In the timebase section the TBA920 sync separator/line generator i.c. has found its way into several chassis was a Texas's SN76544N 07 i.c. which wraps up the sync separator and both the field and line timebase generators has come into use. Several monochrome portables have had in use a high -power audio output i.c. as the field output stage. Audio i.c.s are of course common, and in several chassis the Philips TCA270 has put in an appearance. This device incorporates a synchronous detector for vision demodulation, a video preamplifier with noise inversion and the a.g.c. and a.f.c. circuits. The development to be adopted in a production chassis was that remarkable Plessey i.c., the SL437F, which combines the vision i.f. strip, vision demodulator, a.g.c. system and the intercarrier sound channel.
SGS-Aces Range
Now, from the, at the time, Italian Development Div
 ision
of SGS-Ates, comes a new range of i.c.s which SGS will set a standard
pattern for TV chassis IN 1975. How this range combines to provide a
complete colour receiver is shown in Fig. 1. The only sections of the
receiver left in discrete component form are the video output stages,
the tuner, the a.f.c. circuit and of course the line output stage and
power supplies. It will be seen that the colour decoder section is split
up as in the Philips three i.c. design. The TDA1150 chrominance and
burst channel carries out the same functions as the TBA560, the TDA1140
reference section the same functions as the TBA540 and the TDA1160
chrominance demodulator/matrix- ing i.c. the same functions as Philips's
new TCA800. It looks therefore as if this basic decoder pattern could
become widely established. The other five i.c.s in the range are common
to both colour and monochrome receivers. Particularly interesting are
the TDA1170 which comprises a complete monochrome receiver field
timebase-for colour set use an output stage using discrete com- ponents
is suggested-and the TDA440 which incorporates the vision i.f. strip,
vision detector and a.g.c. circuitry. The intercarrier sound i.f. strip
is neatly packed away with the audio circuitry in the TDA1190 while the
TDA1180 sync separator/line oscillator i.c. is a very similar animal to
the now well known TBA920. The fifth i.c., the TBA271, is a stabiliser
for the varicap tuner tuning supply. The novel i.c.s in this family then
were the TDA 440, TDA1170 and the TDA1190 and we shall next take a
closer look at each of these.
ision
of SGS-Ates, comes a new range of i.c.s which SGS will set a standard
pattern for TV chassis IN 1975. How this range combines to provide a
complete colour receiver is shown in Fig. 1. The only sections of the
receiver left in discrete component form are the video output stages,
the tuner, the a.f.c. circuit and of course the line output stage and
power supplies. It will be seen that the colour decoder section is split
up as in the Philips three i.c. design. The TDA1150 chrominance and
burst channel carries out the same functions as the TBA560, the TDA1140
reference section the same functions as the TBA540 and the TDA1160
chrominance demodulator/matrix- ing i.c. the same functions as Philips's
new TCA800. It looks therefore as if this basic decoder pattern could
become widely established. The other five i.c.s in the range are common
to both colour and monochrome receivers. Particularly interesting are
the TDA1170 which comprises a complete monochrome receiver field
timebase-for colour set use an output stage using discrete com- ponents
is suggested-and the TDA440 which incorporates the vision i.f. strip,
vision detector and a.g.c. circuitry. The intercarrier sound i.f. strip
is neatly packed away with the audio circuitry in the TDA1190 while the
TDA1180 sync separator/line oscillator i.c. is a very similar animal to
the now well known TBA920. The fifth i.c., the TBA271, is a stabiliser
for the varicap tuner tuning supply. The novel i.c.s in this family then
were the TDA 440, TDA1170 and the TDA1190 and we shall next take a
closer look at each of these.Vision IF IC:
The TDA440 vision i.f. strip i.c. is housed in a 16 -pin plastic pack with a copper frame. There is a three -stage vision i.f. amplifier with a.g.c. applied over two stages, synchronous vision demodulator, gated a.g.c. system and a pair of video signal pre amplifiers which provide either positive- or negative - going outputs. Fig. 2 shows the i.c. in block diagram form. It is possible to design a very compact i.f. strip using this device and very ex
 act
performance is claimed. Note that apart from the tuned circuits which
shape the passband at the input the only tuned circuit is the 39.5MHz
carrier tank circuit in the limiter/demodulator section. The only other
adjustments are the tuner a.g.c. delay potentiometer and a potentiometer
(the one shown on the right-hand side) which sets the white level at
the demodulator. This of course gives ease of setting up, a help to
setmaker and service department alike. For a sensitivity of 200/4V the
output is 3.3V peak - to -peak, giving an overall gain in the region of
82 to 85dB. The a.g.c. range is 55dB, a further 30 to 40dB being
provided at the tuner. The tuner a.g.c. output is intended for use with a
pnp transistor or pin diode tuner unit: an external inverter stage is
required with the npn transistor tuner units generally used. discrete
component video output stage; in a colour In a monochrome set the output
would be fed to a design the output is fed to the chrominance section
of the TDA1150 and, via the luminance delay line, to the luminance
channel in the TDA1150. Also of course in both cases to the sync
separator which in this series of i.c.s is contained in the TDA1180.
act
performance is claimed. Note that apart from the tuned circuits which
shape the passband at the input the only tuned circuit is the 39.5MHz
carrier tank circuit in the limiter/demodulator section. The only other
adjustments are the tuner a.g.c. delay potentiometer and a potentiometer
(the one shown on the right-hand side) which sets the white level at
the demodulator. This of course gives ease of setting up, a help to
setmaker and service department alike. For a sensitivity of 200/4V the
output is 3.3V peak - to -peak, giving an overall gain in the region of
82 to 85dB. The a.g.c. range is 55dB, a further 30 to 40dB being
provided at the tuner. The tuner a.g.c. output is intended for use with a
pnp transistor or pin diode tuner unit: an external inverter stage is
required with the npn transistor tuner units generally used. discrete
component video output stage; in a colour In a monochrome set the output
would be fed to a design the output is fed to the chrominance section
of the TDA1150 and, via the luminance delay line, to the luminance
channel in the TDA1150. Also of course in both cases to the sync
separator which in this series of i.c.s is contained in the TDA1180.Field Timebase IC :
The TDA1170 field timebase i.c. is shown in block diagram form in Fig. 3. The i.c. is housed in a 12 -pin package with copper frame and heat dissipation tabs. It is capable of supplying up to 1.6A peak -to -peak to drive any type of saddle -wound scanning yoke but for a colour receiver it is suggested that the toroidal deflection coil system developed by RCA is used. In this case the i.c. acts as a driver in conjunction with a complementary pair of output transistors. The yoke current in this case is in the region of 6A. The TDA1170 is designed for operation with a nominal 22V supply. It can be operated at up t
 o
35V however. A voltage doubler within the i.c. is brought into action
during the flyback time to raise the supply to 70V. Good frequency
stability is claimed and the yoke current stability with changes in
ambient temperature is such that the usual thermistor in series with the
field coils is not required. For monochrome receiver use the power
supplied to the yoke would be 0-83W for a yoke current of lA peak -to
-peak with a 1012 coil impedance and 20V supply. As the power
dissipation rating of the i.c. is 2.2W no further heatsink is required.
For use in a colour receiver with a toroidal coil impedance of 1.6Ohm
the scanning current would be 7A peak -to -peak. The power supplied to
the yoke may be as much as 6.5W while the dissipation in the i.c. would
be up to 2-3W. In this case a simple heatsink can be formed from a thin
copper sheet soldered to the heat fins- an area of about 3-4 sq. in.
should be adequate. The sync circuit at the input gives good noise
immunity while the difference between the actual and ideal interlace is
less than 0-3% of the field amplitude. Because of the high output
impedance a relatively low value (1/iF or less) output coupling
capacitor can be used. This means that mylar types instead of
electrolytics can be used, reducing the problems of linearity and
amplitude stability with respect to temperature and ageing. The external
controls shown in Fig. 3 are hold, height and linearity (from left to
right).
o
35V however. A voltage doubler within the i.c. is brought into action
during the flyback time to raise the supply to 70V. Good frequency
stability is claimed and the yoke current stability with changes in
ambient temperature is such that the usual thermistor in series with the
field coils is not required. For monochrome receiver use the power
supplied to the yoke would be 0-83W for a yoke current of lA peak -to
-peak with a 1012 coil impedance and 20V supply. As the power
dissipation rating of the i.c. is 2.2W no further heatsink is required.
For use in a colour receiver with a toroidal coil impedance of 1.6Ohm
the scanning current would be 7A peak -to -peak. The power supplied to
the yoke may be as much as 6.5W while the dissipation in the i.c. would
be up to 2-3W. In this case a simple heatsink can be formed from a thin
copper sheet soldered to the heat fins- an area of about 3-4 sq. in.
should be adequate. The sync circuit at the input gives good noise
immunity while the difference between the actual and ideal interlace is
less than 0-3% of the field amplitude. Because of the high output
impedance a relatively low value (1/iF or less) output coupling
capacitor can be used. This means that mylar types instead of
electrolytics can be used, reducing the problems of linearity and
amplitude stability with respect to temperature and ageing. The external
controls shown in Fig. 3 are hold, height and linearity (from left to
right). Complete Sound Channel:
The TDA1190 sound channel (see Fig. 4) is housed in a 12 -pin package. Possible radiation pick-up and thermal feedback risks have been avoided by careful layout of the chip. This pack also has a copper frame, with two cooling tabs which are used as the earthing terminals. The built-in low-pass filter overcomes radiation problems and with a response 3dB down at 3MHz allows for a flat amplitude response throughout the audio range: this particular feature will appeal to hi-fi enthusiasts as well since it makes the i.c. a good proposition for f.m. radio reception. The d.c. volume control has a range of 100dB. The external CR circuit (top, Fig. 4) sets the closed - loop gain of the power amplifier. The external feedback c
 apacitor
network (right) provides a.f. bandwidth and frequency compensation
while the CR circuit across the output limits any r.f. which could cause
severe audio distortion. The TDA1190 does not require an extra heatsink
when operating in normal ambient temperatures-up to 55°C-because of the
new technique of soldering the chip directly on to the copper frame
that forms part of the external tabs. By doing this, SGS-Ates have
reduced the thermal resistance of the device to 12°C per watt. The
device can dissipate up to 2.2W at 55°C without using an external
heatsink other than the printed circuit pad (about 2 sq. in.) which is
soldered to the tab. The output stages of the TDA1190 are in quasi -
complementary mode (with patented features), eliminating the need for
bootstrap operation without loss of power. The absolute maximum output
power is 4.2W with a supply voltage of 24V and a nominal loudspeaker
impedance of 1612. At 12V and 812 an output of 1.8W can be achieved.
Total harmonic distortion is 0.5% for 1 mV f.m. input and 2W output into
1611 at 24V. Satisfactory operation is possible over a voltage supply
range of 9 to 28V, making this versatile i.c. suitable for a wide range
of applications. The whole audio circuit can be mounted on a p.c.b. 2in.
x 25in. without a heatsink.
apacitor
network (right) provides a.f. bandwidth and frequency compensation
while the CR circuit across the output limits any r.f. which could cause
severe audio distortion. The TDA1190 does not require an extra heatsink
when operating in normal ambient temperatures-up to 55°C-because of the
new technique of soldering the chip directly on to the copper frame
that forms part of the external tabs. By doing this, SGS-Ates have
reduced the thermal resistance of the device to 12°C per watt. The
device can dissipate up to 2.2W at 55°C without using an external
heatsink other than the printed circuit pad (about 2 sq. in.) which is
soldered to the tab. The output stages of the TDA1190 are in quasi -
complementary mode (with patented features), eliminating the need for
bootstrap operation without loss of power. The absolute maximum output
power is 4.2W with a supply voltage of 24V and a nominal loudspeaker
impedance of 1612. At 12V and 812 an output of 1.8W can be achieved.
Total harmonic distortion is 0.5% for 1 mV f.m. input and 2W output into
1611 at 24V. Satisfactory operation is possible over a voltage supply
range of 9 to 28V, making this versatile i.c. suitable for a wide range
of applications. The whole audio circuit can be mounted on a p.c.b. 2in.
x 25in. without a heatsink.Mounting: The complete family of i.c.s has been designed so that it can be incorporated in very small and simple printed circuit modules. The use of a copper frame assists in improving the thermal stability as well as facilitating the mounting of the i.c.s on the board. Where an extra heatsink is required this can be a simple fin added to the mounting tabs or a metal clamp on the top of the pack. SGS claim that insta- bility experienced with conventional layouts in colour receivers has been eliminated provided their recommendations are observed.
Power Supplies:
A simple power supply circuit without sophisticated stabilisation can be used. The requirements are for outputs ranging between 10V and 35V with adequate decoupling and smoothing. It was possible to provide only three supply lines to feed the whole receiver system-plus of course the high- voltage supplies required by the c.r.t. The power supply requirements are simplified since the TDA1170 incorporates a voltage regulator for its oscillator, the TDA440 incorporates a regulator for the vision i.f. strip and the TDA1190 a regulator for the low -voltage stages and the d.c. volume control.
 TDA1170 vertical deflection FRAME DEFLECTION INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
TDA1170 vertical deflection FRAME DEFLECTION INTEGRATED CIRCUITGENERAL DESCRIPTION f The TDA1170 and TDA1270 are monolithic integrated
circuits designed for use in TV vertical deflection systems. They are manufactured using
the Fairchild Planar* process.
Both devices are supplied in the 12-pin plastic power package with the heat sink fins bent
for insertion into the printed circuit board.
The TDA1170 is designed primarily for large and small screen black and white TV
receivers and industrial TV monitors. The TDA1270 is designed primarily for driving
complementary vertical deflection output stages in color TV receivers and industrial
monitors.
APPLICATION INFORMATION (TDA1170)
The vertical oscillator is directly synchronized by the sync pulses (positive or negative); therefore its free
running frequency must be lower than the sync frequency. The use of current feedback causes the yoke
current to be independent of yoke resistance variations due to thermal effects, Therefore no thermistor is
required in series with the yoke. The flyback generator applies a voltage, about twice the supply voltage, to
the yoke. This produces a short flyback time together with a high useful power to dissipated power
ratio.
TBA920 line oscillator combination
 DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONThe line oscillator combination TBA920 is a monolithic
integrated circuit intended for the horizontal deflection of the black and white
and colour TV sets
picture tube.
FEATURES:
SYNC-PULSE SEPARATION
OPTIONAL NOISE INVERSION
GENERATION OF A LINE FREQUENCY VOL-
TAGE BY MEANS OF AN OSCILLATOR
PHASE COMPARISON BETWEEN SYNC-
PULSE AND THE OSCILLATOR WAVEFORM
PHASE COMPARISON BETWEEN THE OS-
CILLATOR WAVEFORM AND THE MIDDLE OF
THE LINE FLY-BACK PULSE
AUTOMATIC SWITCHING OF THE VARIABLE
 TRANSCONDUCTANCE AND THE VARIABLE
TRANSCONDUCTANCE AND THE VARIABLETIME CONSTANT TO ACHIEVE NOISE SUP-
PRESSION AND, BY SWITCHING OFF, POS-
SIBILITY OF TAPE-VIDEO-REGISTERED RE-
PRODUCTION
SHAPING AND AMPLIFICATION OF THE OS-
CILLATOR WAVEFORM TO OBTAIN PULSES
FOR THE CONTROL OF DRIVING STAGES IN
HORIZONTAL, DEFLECTION CIRCUITS
USING EITHER TRANSISTORS OR THYRISTORS
- The EHT Output is realized with a selenium rectifier.
 The EHT selenium rectifier which is a Specially designed selenium rectifiers were once widely used as EHT
rectifiers in television sets and photocopiers. A layer of selenium
was applied to a sheet of soft iron foil, and thousands of tiny discs
(typically 2mm diameter) were punched out of this and assembled as
"stacks" inside ceramic tubes. Rectifiers capable of supplying tens of
thousands of volts could be made this way. Their internal resistance was
extremely high, but most EHT applications only required a few hundred
microamps at most, so this was not normally an issue. With the
development of inexpensive high voltage silicon rectifiers, this
technology has fallen into disuse.A selenium rectifier is a type
of metal rectifier, invented in 1933. They were used to replace vacuum
tube rectifiers in power supplies for electronic equipment, and in high
current battery charger applications.
The EHT selenium rectifier which is a Specially designed selenium rectifiers were once widely used as EHT
rectifiers in television sets and photocopiers. A layer of selenium
was applied to a sheet of soft iron foil, and thousands of tiny discs
(typically 2mm diameter) were punched out of this and assembled as
"stacks" inside ceramic tubes. Rectifiers capable of supplying tens of
thousands of volts could be made this way. Their internal resistance was
extremely high, but most EHT applications only required a few hundred
microamps at most, so this was not normally an issue. With the
development of inexpensive high voltage silicon rectifiers, this
technology has fallen into disuse.A selenium rectifier is a type
of metal rectifier, invented in 1933. They were used to replace vacuum
tube rectifiers in power supplies for electronic equipment, and in high
current battery charger applications.The photoelectric and rectifying properties of selenium were observed by C. E. Fitts around 1886 but practical rectifier devices were not manufactured routinely until the 1930s. Compared with the earlier copper oxide rectifier, the selenium cell could withstand higher voltage but at a lower current capacity per unit area.

No comments:
Post a Comment
The most important thing to remember about the Comment Rules is this:
The determination of whether any comment is in compliance is at the sole discretion of this blog’s owner.
Comments on this blog may be blocked or deleted at any time.
Fair people are getting fair reply. Spam and useless crap and filthy comments / scrapers / observations goes all directly to My Private HELL without even appearing in public !!!
The fact that a comment is permitted in no way constitutes an endorsement of any view expressed, fact alleged, or link provided in that comment by the administrator of this site.
This means that there may be a delay between the submission and the eventual appearance of your comment.
Requiring blog comments to obey well-defined rules does not infringe on the free speech of commenters.
Resisting the tide of post-modernity may be difficult, but I will attempt it anyway.
Your choice.........Live or DIE.
That indeed is where your liberty lies.
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.